Digitalizing the procurement function is a strategic lever for all companies, regardless of size or industry. Between the search for efficiency, cost control, and risk management, procurement software has become central to organizational transformation. Yet with the multitude of available solutions, navigating this landscape is not always easy.
Understanding these different categories of tools is essential to choosing the right solution for your organization, especially when dealing with professional services, a complex and strategic procurement category marked by high legal risks, the coordination of numerous stakeholders, and recurring activities that require rigorous follow-up.
ERPs: the backbone of the information system
ERPs (Enterprise Resource Planning) centralize financial, accounting, and HR data. Their procurement modules help structure processes and ensure compliance, as is the case with widely deployed solutions such as SAP, Oracle, or Microsoft Dynamics.
They offer a global and integrated approach but often remain rigid and not well suited to the agility required by procurement teams, particularly for professional services, where flexibility and precise mission management are essential.
E-procurement solutions: automating transactions
E-procurement tools digitalize the entire Procure-to-Pay (P2P) cycle, meaning the complete process from internal request to supplier payment.
Concretely, P2P includes: procurement requests, validation, order management, receipt of goods or services, as well as invoice processing and matching.
These transactional procurement solutions can also integrate upstream stages such as sourcing and ensure better traceability, strengthened budget compliance, and smoother management of all procurement operations.
However, their approach remains primarily designed for procurement teams. These platforms work very well for standardized procurement categories but are less suited to professional services, a more specific category that relies on qualitative elements such as mission definition, deliverable management, or consultant follow-up.
They are particularly effective for managing administrative and financial processes but may be less adapted to operational needs. Their ergonomics, designed for global control, sometimes meet daily business needs less effectively, as teams require more flexibility in managing their missions, deliverables, or service providers.
These limitations highlight the complementarity between e-procurement and Vendor Management Systems (VMS). VMS extend the existing setup by handling the specific needs of professional services, such as mission, deliverable, or supplier follow-up.
To know more about their complementarity, check this article.
Vendor Management Systems: the dedicated solution for professional services
Vendor Management Systems (VMS) are platforms specialized in managing professional services and external service providers.
They cover the full Source-to-Pay (S2P) cycle: sourcing, contracting, mission follow-up, time validation, invoicing, and performance analysis, whether for IT or non-IT services, delivered in time-and-materials or fixed-price models.
Their added value lies in their ability to manage complex, multi-vendor, and multi-entity environments while ensuring legal compliance and budget visibility.
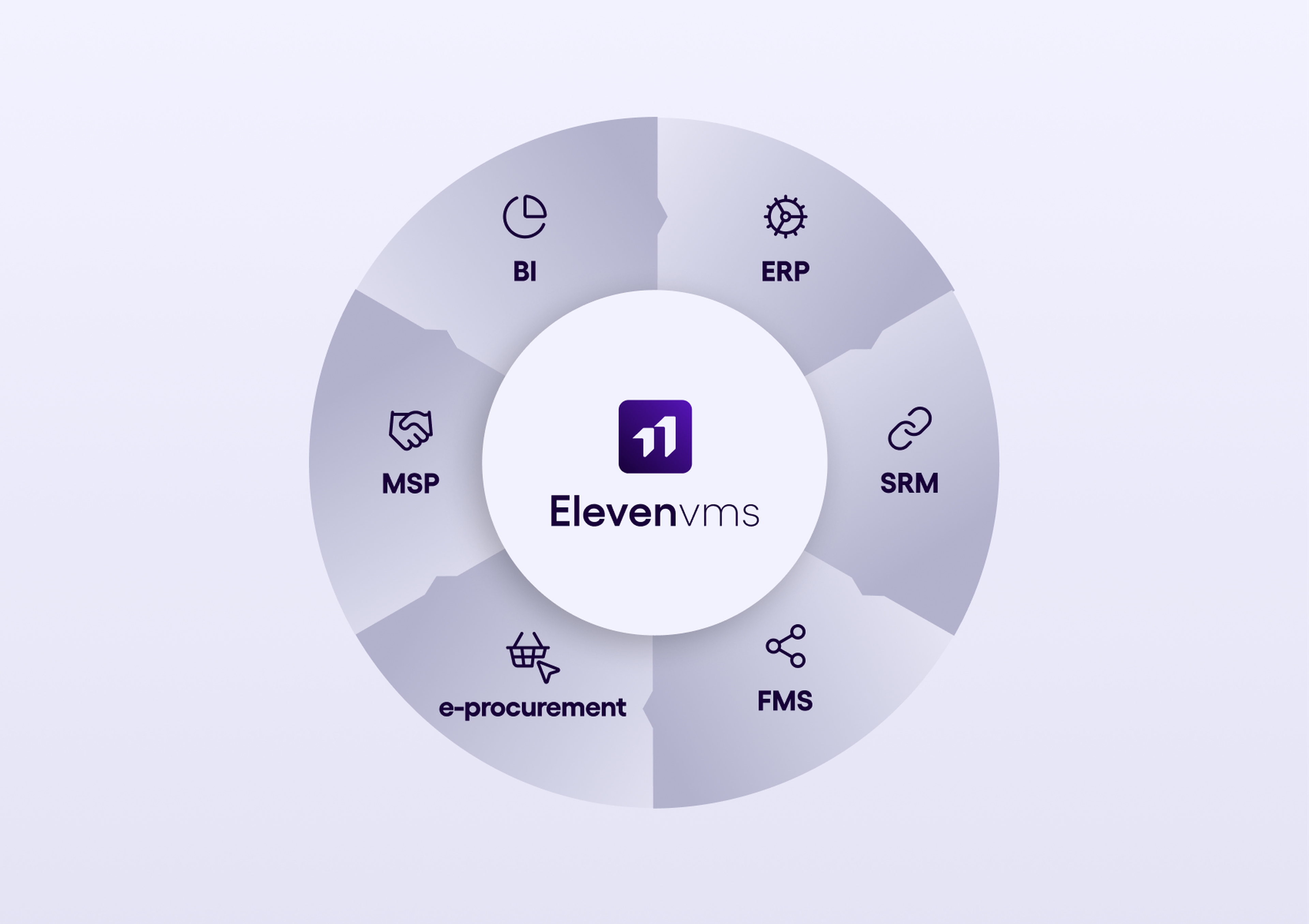
Designed to integrate naturally into each client’s ecosystem, VMS adapt both to existing architecture and to operational realities. Their flexibility allows them to fit smoothly into established processes without disrupting user habits, while unifying practices and data within a single platform.
A modern VMS, such as Eleven VMS, enables organizations to:
Centralize and manage all service providers and mission lifecycles, including fixed-price engagements and deliverables, while applying procurement rules (framework agreements, rate cards, workflows, competitive bidding).
Automate administrative tasks and budget tracking.
Manage procurement and supplier performance, supported by advanced reporting modules and artificial intelligence capabilities to anticipate needs and optimization opportunities.
By placing professional services at the heart of its design, a VMS transforms a domain often perceived as complex into a lever for agility, performance, and strategic control.
SRM: managing supplier relationships
Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) tools focus on managing and ensuring the quality of the supplier relationship.
They support the monitoring of performance, compliance, ESG commitments, and collaboration.
These tools are often used alongside a VMS to structure interactions and strengthen supplier governance.
Spend Management and Business Intelligence tools
Spend Management solutions analyze procurement spend and identify savings opportunities.
They offer a strategic view of procurement performance by leveraging data to guide decisions and improve overall efficiency.
They form the essential analytical layer of a mature procurement ecosystem.
International tools
Globally, the procurement ecosystem has evolved with the emergence of new models and players, particularly around external workforce management.
These tools often complement more traditional solutions and reflect different organizational approaches depending on the region.
Professional services procurement models vary geographically. Some markets prioritize technology, while others rely on external operators.
Managed Service Providers
Though not software solutions, MSPs belong to the information system logic as external providers specialized in governance and management of professional services procurement.
They take charge of operating a VMS, managing suppliers, ensuring compliance, contracting, and sometimes even sourcing.
Widespread in North America and the UK, the MSP model primarily targets large international companies seeking to centralize the management of their contingent workforce while leveraging external expertise.
Technology platforms: FMS, CWM, and marketplaces
Freelancer Management Systems (FMS) address the rise of independent work.
They enable companies to manage freelancers directly: sourcing, contracting, compliance, and payment.
The VMS manages supplier relationships (consultancies, IT services firms), while the FMS manages direct relationships with talent.
This boundary is becoming blurred with the emergence of Contingent Workforce Management (CWM) platforms, which unify all external workforce management in a single interface.
Global B2B marketplaces are also increasingly used for sourcing professional services.
They provide access to a global pool of service providers while integrating features similar to VMS solutions, such as compliance management or performance tracking.
They complete the ecosystem: marketplaces expand access to resources, while the VMS ensures governance and control.
The central role of the VMS in this ecosystem
Within this rich ecosystem, the Vendor Management System (VMS) plays a central role by centralizing providers, automating key processes, and ensuring compliance while interfacing with the other components of the procurement information system.
By connecting with SRM, e-procurement, or Business Intelligence tools, the VMS consolidates data, strengthens process coherence, and becomes the foundation for global professional services management.
Designed for procurement but also for operational teams, the VMS ties together the operational and strategic dimensions of external collaboration, turning professional services into a measurable performance lever.
Eleven VMS illustrates this modern approach: an open, intuitive, and connected platform capable of managing all forms of professional services, whether delivered by consultancies, IT services firms, or freelancers.
It simplifies daily complexity and strengthens control at every stage of a mission’s lifecycle.
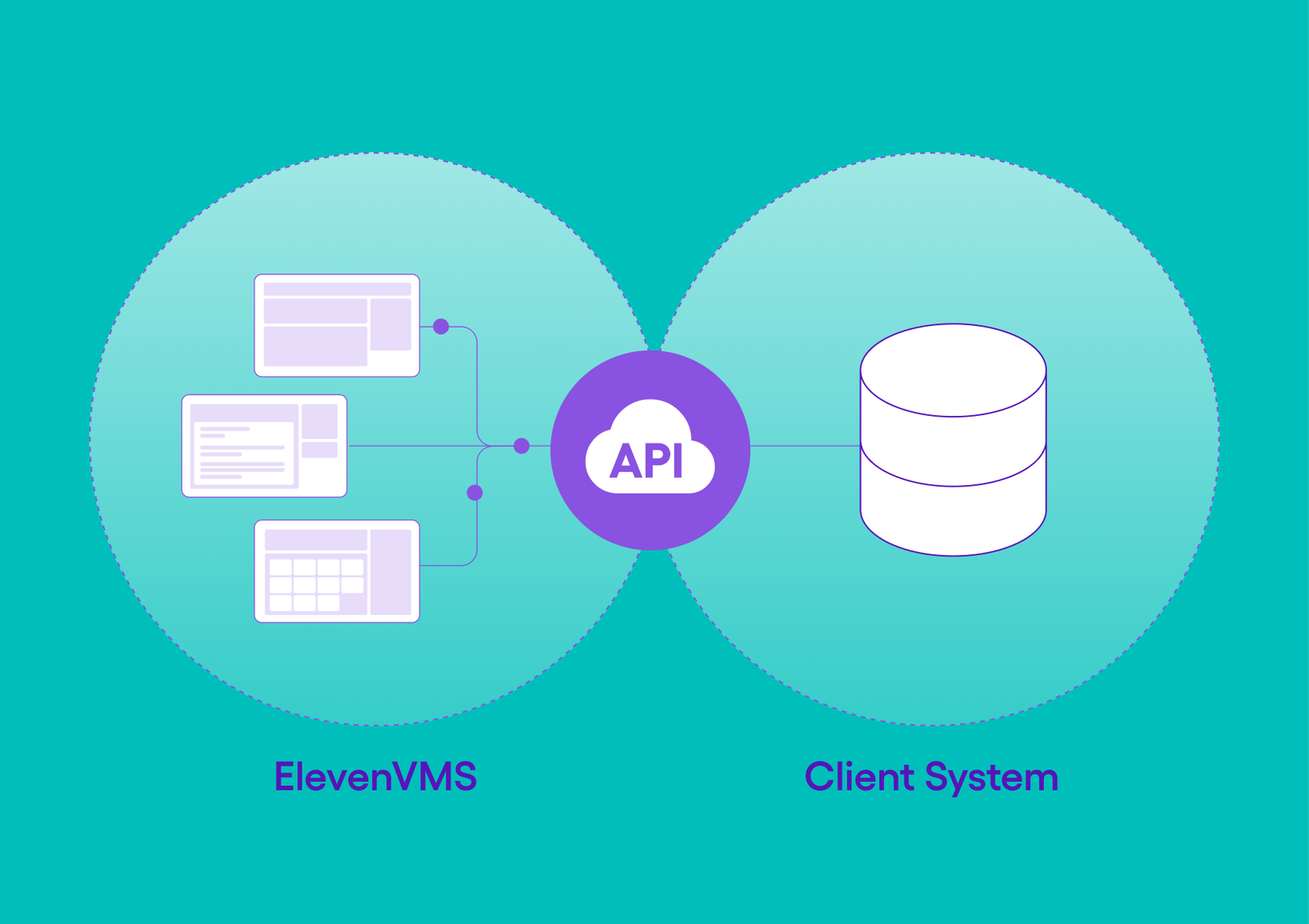
Thanks to its native integration capabilities with major market solutions such as SAP, Coupa, or Corcentric, Eleven VMS naturally fits into any existing procurement ecosystem, ensuring smooth data flows and continuity across the information system.
Conclusion
In a market where tools are multiplying, the challenge is no longer simply to digitalize procurement but to build a coherent ecosystem suited to the realities of each organization.
The Vendor Management System stands out as an agile component, the one that connects existing tools and aligns procurement strategy, operational performance, and management of professional services.
It has become a genuine transformation lever for procurement teams, capable of unifying processes, teams, and data around a shared vision of performance.
Interested in discussing your procurement challenges or assessing your current ecosystem?
Our Eleven VMS experts can support you in building a strategy aligned with your priorities.